- Contents
- Index
- Quick Start Guide in 3 Steps
- Features
- Advanced Options
- Definitions
- Contact and Support
- System Requirements
© 2025 R-Tools Technology Inc.
All rights reserved.
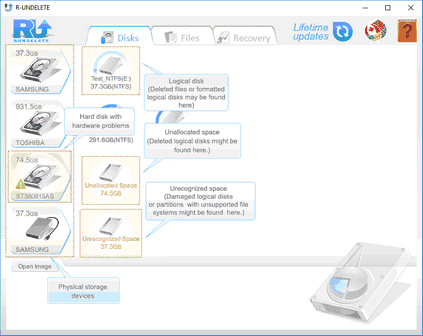
Step 1. Disk Selection
• Locate the physical storage device where lost files resided.
|
|
Computer's internal hard drives . Disks with files reside on them. |
|
|
USB storage devices like external hard drives or memory sticks |
|
|
SSD storage devices . File recovery from such devices has some peculiarities described in the SSD and NVME storage devices section. |
|
|
NVME storage devices. SSD storage devices connected to the computer through a special interface. They have the same file recovery peculiarities of SSD devices described in the SSD and NVME storage devices section. |
|
|
Disk image . A file that contains exact, byte by byte, copies of storage devices or disks. Files from such images can be recovered as if those images were real disks. |
|
|
CD/DVD discs or virtual disks. |
• Check if the hardware of the storage device with lost files is not in a bad condition.
If the storage device has hardware problems, R‑Undelete marks such a device with an exclamation check and gives a S.M.A.R.T. Monitoring warning. Disk imaging is the best solution in this situation.
• Select the disk on the device where the lost files might reside.
Recovery of deleted files or lost files from a formatted disk with the same file system
These files most likely reside on an existing disk.
To see the files resided on the disk, right-click and select Show Files ( Quick Scan operation ). Depending on the disk sizes, the number of files, and your computer hardware, it may take a few seconds or more. When files are found, R‑Undelete switches to the Files panel where found files are selected for recovery .
Recovery of lost files from a formatted disk with a different file system
These files most likely reside on an existing disk.
To see the files resided on the formatted disk, right-click and select Show Files ( Quick Scan operation ). Depending on the disk size, the number of files, and your computer hardware, it may take a few seconds or more. When R‑Undelete switches to the Files panel, click the Deep scan button, wait for Deep Scan to finish, and select the previous partition where lost files resided. Then select files for recovery .
Recovery of lost files from a deleted disk
Deleted disks are usually found on the unallocated space.
Right-click the unallocated space on the storage device of the disk, select Scan for partitions, and wait for R‑Undelete to finish scanning the device. Note that it may take a long time if the device is large. When the disk is found, right-click Show Files then select files for recovery .
Recovery of lost files from a damaged disk or a partition with an unsupported file system
Damaged disks or partitions with unsupported file system are usually found on the unrecognized space.
This recovery is very similar to the case of lost files from a deleted disk.
Right-click the unrecognized space on the storage device of the disk, select Scan, and wait for R‑Undelete to finish scanning the device. Note that it may take a long time if the device is large. When the disk or a partition is found, right-click Show Files then select files for recovery .
If the files are to be recovered from a partition with an unsupported files system, R‑Undelete will use only raw file search , and, therefore, will not recover file names and the original folder structure. See the Definitions help page for more details.
![]() Disks,Unrecognized Space, and Unallocated Space Icons
Disks,Unrecognized Space, and Unallocated Space Icons
|
|
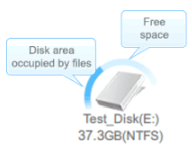
A logical disk with letter (E:). Deleted files or files from formatted disks might reside on such disks. |
|
|
Unallocated space on a storage devices. A storage space that does not belong to any disk. A deleted disk (partition) might be found here. |
|
|
Unrecognized space on a storage devices. A storage space that is supposed to belong to a disk or partition, but R‑Undelete cannot detect any because of its damaged or unsupported file system. A damaged disk or a partition with an unsupported file system might be found here. |
|
|
A partition on a hard drive encrypted using the BitLocker feature. R‑Undelete can recover files from such partitions it they are decrypted by the system. |
- R-Studio Technician: activation using a USB stick
- Data Recovery Guide
- Why R-Studio?
- R-Studio for Forensic and Data Recovery Business
- R-STUDIO Review on TopTenReviews
- File Recovery Specifics for SSD devices
- How to recover data from NVMe devices
- Predicting Success of Common Data Recovery Cases
- Recovery of Overwritten Data
- Emergency File Recovery Using R-Studio Emergency
- RAID Recovery Presentation
- R-Studio: Data recovery from a non-functional computer
- File Recovery from a Computer that Won't Boot
- Clone Disks Before File Recovery
- HD Video Recovery from SD cards
- File Recovery from an Unbootable Mac Computer
- The best way to recover files from a Mac system disk
- Data Recovery from an Encrypted Linux Disk after a System Crash
- Data Recovery from Apple Disk Images (.DMG files)
- File Recovery after Re-installing Windows
- R-Studio: Data Recovery over Network
- How To Use R-Studio Corporate Package
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted NTFS Disk
- Data Recovery from an ReFS disk
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted exFAT/FAT Disk
- Data Recovery from an Erased HFS Disk
- Data Recovery from an Erased APFS Disk
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted Ext2/3/4FS Disk
- Data Recovery from an XFS Disk
- Data Recovery from a Simple NAS
- How to connect virtual RAID and LVM/LDM volumes to the operating system
- Specifics of File Recovery After a Quick Format
- Data Recovery After Partition Manager Crash
- File Recovery vs. File Repair
- Data Recovery from Virtual Machines
- How to Recover Files from a Remote Computer Using R-Studio Standalone License and Its Network Capabilities in Demo Mode
- How to Connect Disks to a Computer
- Emergency Data Recovery over Network
- Data Recovery over the Internet
- Creating a Custom Known File Type for R-Studio
- Finding RAID parameters
- Recovering Partitions on a Damaged Disk
- NAT and Firewall Traversal for Remote Data Recovery
- Data Recovery from an External Disk with a Damaged File System
- File Recovery Basics
- Default Parameters of Software Stripe Sets (RAID 0) in Mac OS X
- Data Recovery from Virtual Hard Disk (VHD/VHDX) Files
- Data Recovery from Various File Container Formats and Encrypted Disks
- Automatic RAID Parameter Detection
- IntelligentScan Data Recovery Technology
- Multi-pass imaging in R-Studio
- Runtime Imaging in R-Studio
- Linear Imaging vs Runtime Imaging vs Multi-Pass Imaging
- USB Stabilizer Tech for unstable USB devices
- Joint work of R-Studio and PC-3000 UDMA hardware
- Joint work of R-Studio and HDDSuperClone
- R-Studio T80+ - A Professional Data Recovery and Forensic Solution for Small Business and Individuals Just for 1 USD/day
- Backup Articles
- R-Drive Image Standalone and Corporate license transferring
- Fixing Windows update error 0x80070643 with R-Drive Image
- Backup with Confidence
- R-Drive Image as a free powerful partition manager
- Computer Recovery and System Restore
- Disk Cloning and Mass System Deployment
- Accessing Individual Files or Folders on a Backed Up Disk Image
- R-Drive Image startup / bootable version
- File Backup for Personal Computers and Laptops of Home and Self-Employed Users
- Creating a Data Consistent, Space Efficient Data Backup Plan for a Small Business Server
- How to Move the Already Installed Windows from an Old HDD to a New SSD Device and Create a Hybrid Data Storage System
- How to Move an Installed Windows to a Larger Disk
- How to Move a BitLocker-Encrypted System Disk to a New Storage Device
- How to backup and restore disks on Linux and Mac computers using R-Drive Image
- R-Drive Image and Virtual Machines
- Undelete Articles
- Get Deleted Files Back
- Free Recovery from SD and Memory cards
- R-Undelete: Video Recovery
- Recovery from an External Device with a Damaged File System
- File recovery from a non-functional computer
- Free File Recovery from an Android Phone Memory Card
- Free Photo and Video File Recovery Tutorial
- Easy file recovery in three steps